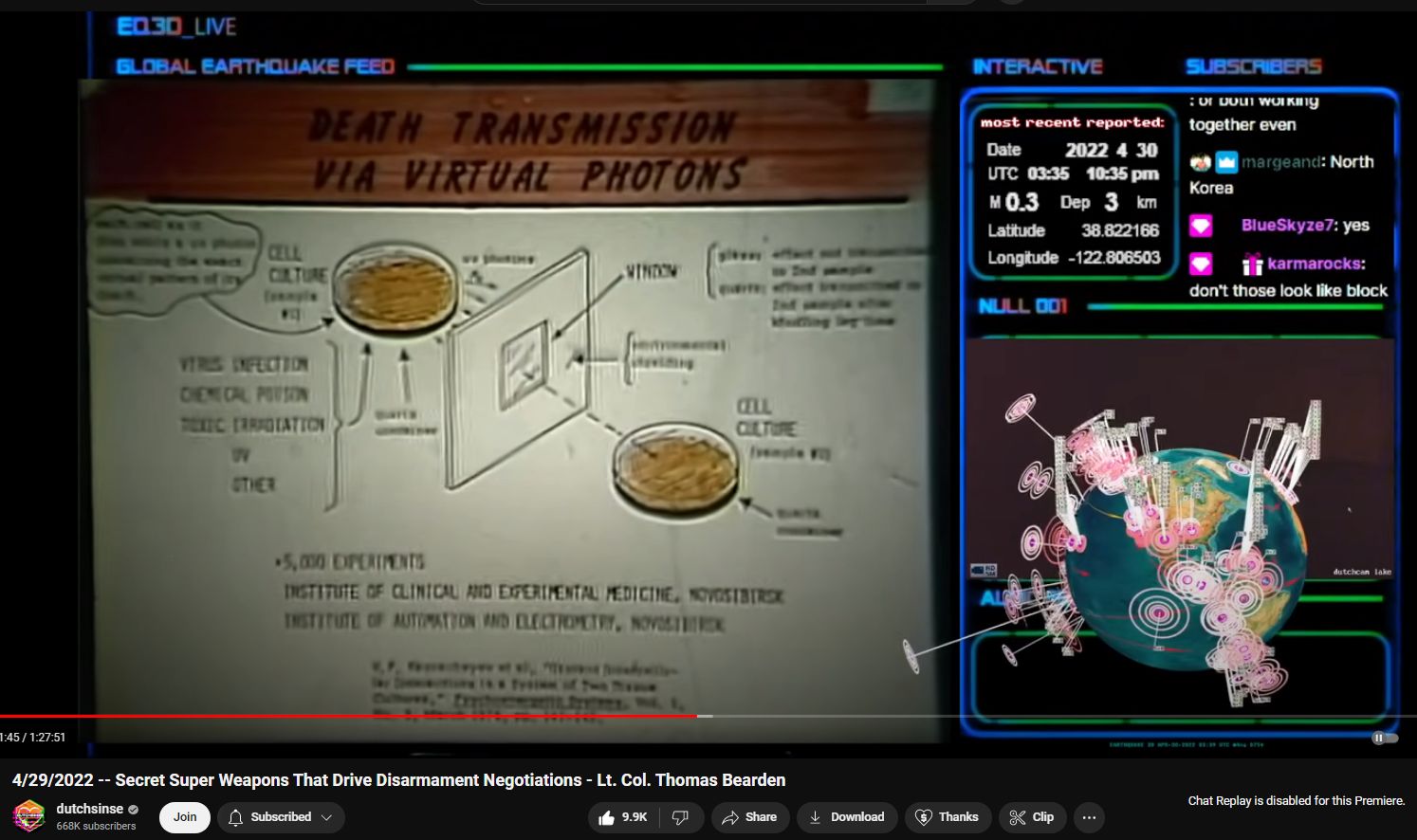
Death and Disease Transmission via Virtual Photons Apparently Radio Waves Can Transmit Disease
41:30 into video
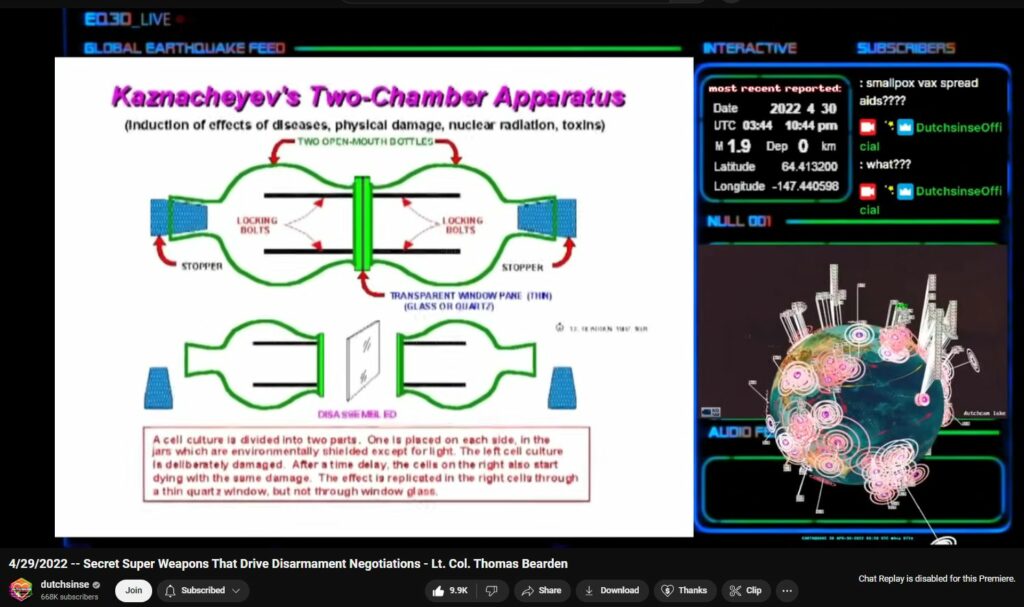
The experiments in Novosibirsk during the 1960s, often attributed to the research of Dr. Vlail Kaznacheyev, explored the possibility of electromagnetic transmission of disease. These studies were conducted at the Institute of Clinical and Experimental Medicine in Novosibirsk, part of the Soviet Union’s extensive biophysical research efforts during the Cold War.
The experiments in Novosibirsk during the 1960s, often attributed to the research of Dr. Vlail Kaznacheyev, explored the possibility of electromagnetic transmission of disease. These studies were conducted at the Institute of Clinical and Experimental Medicine in Novosibirsk, part of the Soviet Union’s extensive biophysical research efforts during the Cold War.
Key Features of the Experiments:
- Setup:
- The researchers used two identical cultures of living cells placed in sealed, separate but optically connected chambers.
- One culture (the “source”) was deliberately infected or exposed to harmful agents such as toxins, pathogens, or radiation.
- The other culture (the “receiver”) was healthy and unexposed to any physical contaminants from the source.
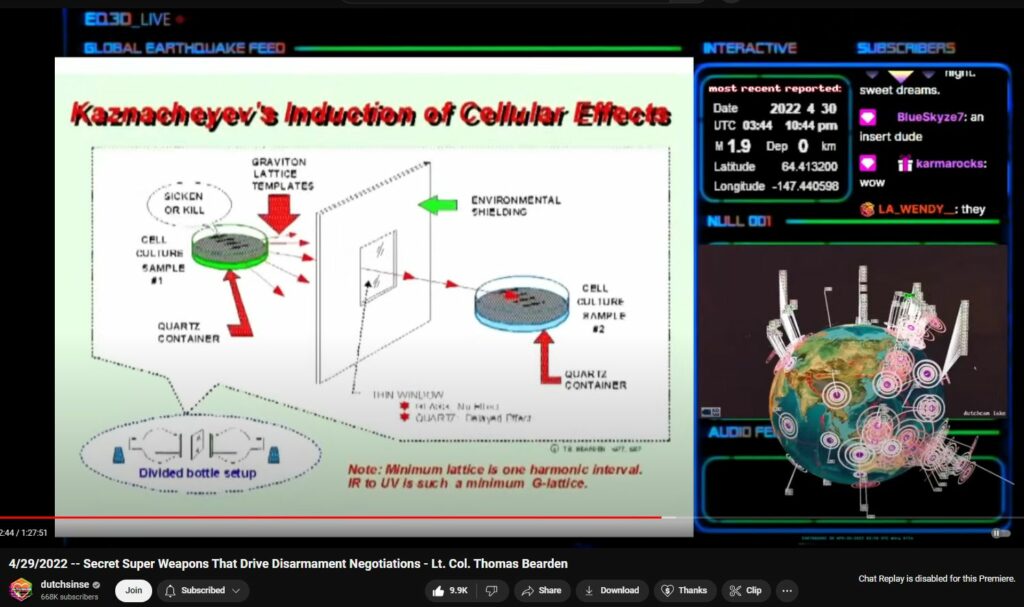
- Optical Connection:
- The chambers were separated by a quartz window that allowed only ultraviolet (UV) light to pass through.
- UV light was believed to act as a carrier for information or “signals” between the infected and healthy cultures.
- Findings:
- Remarkably, the healthy cultures in the receiver chamber began to show signs of the same damage or disease as the infected cultures in the source chamber.
- The transmission occurred without direct physical contact or the transfer of chemical agents.
- Hypothesis:
- The researchers proposed that the disease transmission occurred via electromagnetic waves, particularly in the UV spectrum.
- They speculated that cells emit biophotons—ultra-weak light emissions—that carry biological information, possibly even patterns of disease.
- Implications:
- The experiments suggested that diseases or cellular states could be transmitted via electromagnetic signals, challenging the traditional biochemical understanding of pathology.
- This sparked theories about a possible biofield or an underlying informational component to living systems, influencing fields like energy medicine and biophysics.
Legacy and Controversy:
- While groundbreaking, the results were and remain controversial. Critics argued that replication of these findings was inconsistent and that other factors, like experimental error or contamination, might explain the observed effects.
- The experiments have been cited in support of pseudoscientific claims and speculative technologies, including scalar wave medicine, energy healing, and non-local biological effects.
Modern Connections:
The work aligns with current interest in biophoton research and the concept of cells communicating through light emissions. Though still on the fringe of mainstream science, it has inspired exploration into the role of electromagnetic fields in health, disease, and cellular communication.
If you’re interested in further details or related experiments, feel free to ask!
Robert O Becker went on to write BODY ELECTRIC
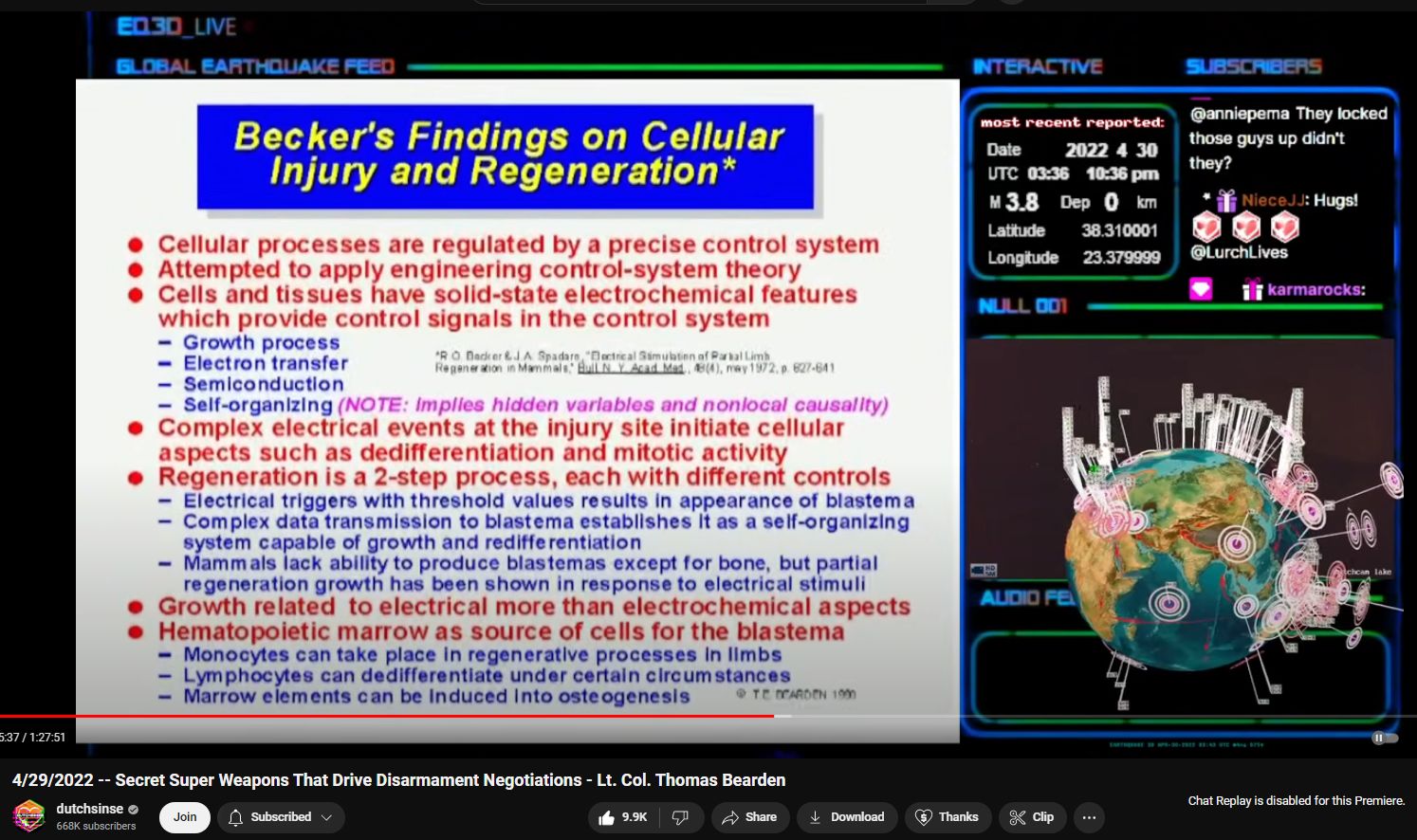
“Cellular changes are most certainly induceable and controllable electromagnetically by miniscule amounts of potentials and currents.” 46:00 in